

It is based on where pulmonary arteries arise from the common trunk. The Collett and Edwards system is the earliest form of classification, developed in 1949. Type I/A1 is the most common form, found in ~60% of patients with Truncus Arteriosus. There are four subtypes of truncus arteriosus which are described using two different classification systems (outlined below). In Nichols DG, Ungerleider RM, Spevak PJ, et al : Critical heart disease in infants and children, Philadelphia, 2006, Mosby, p 690.) (Adapted from St Louis, JD: Persistent truncus arteriosus. Ao, ascending aorta LPA, left pulmonary artery MPA, main pulmonary artery RPA, right pulmonary artery. Coronary artery anomalies seen in TA cases include atypical origin, single coronary, or narrowed ostia resulting in coronary stenosis.įigure 1: Classifications of truncus arteriosus.

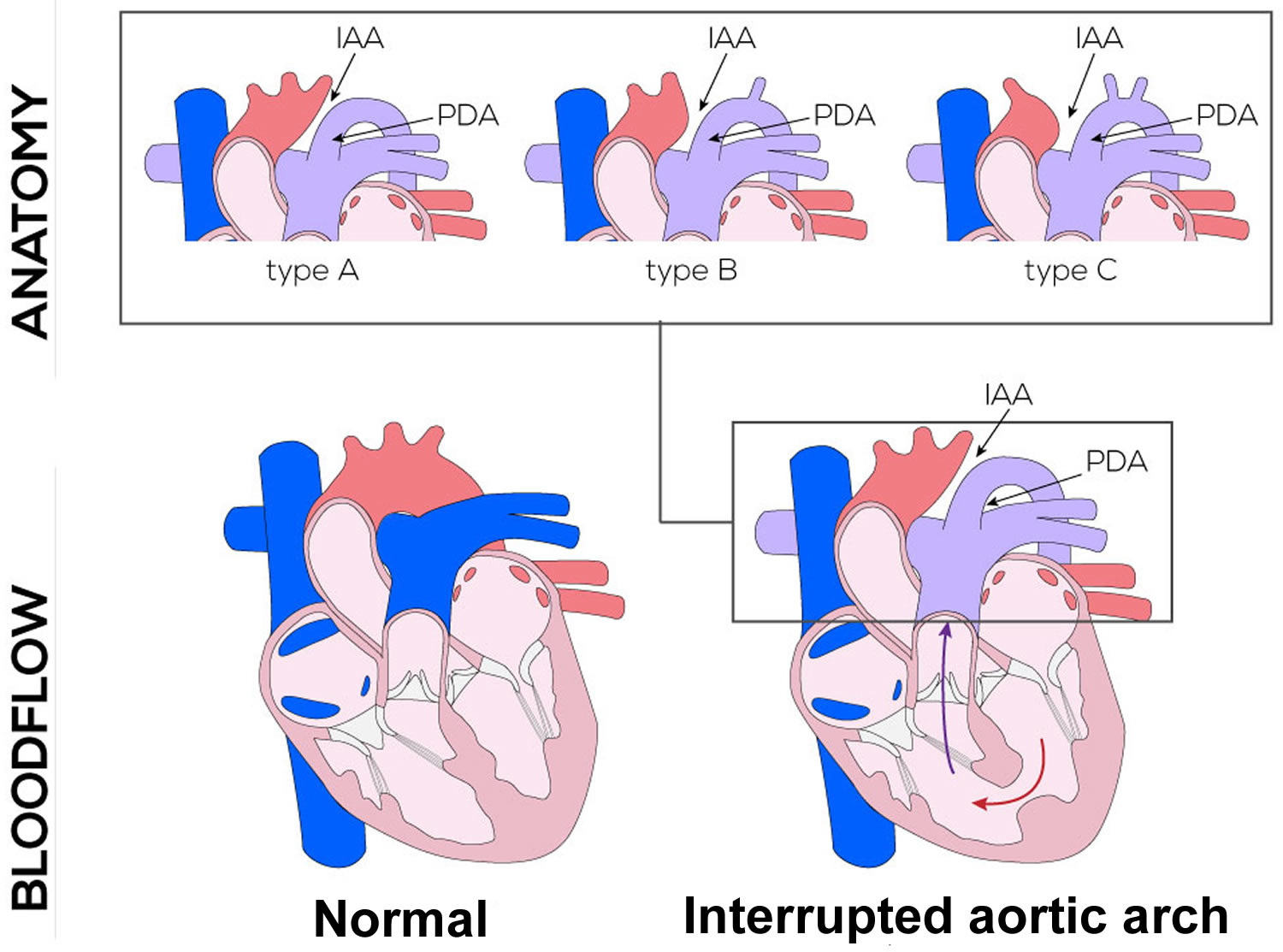
The valve is most commonly tricuspid, but may also be bicuspid, quadricuspid or pentacuspid (rare) valve.Īpproximately 30% of patients with TA have a right aortic arch and 10-12% have aortic arch hypoplasia or an interrupted aortic arch. Truncal valve leaflets are usually thickened. A VSD is present in the vast majority of cases. It may be confused with PA-VSD or aortic atresia with VSD on fetal cardiac evaluation, because one of the great arteries in those conditions is severely hypoplastic.Ī ventricular septal defect (VSD) is most commonly associated with TA, as well as anomalies with truncal valve, aortic arch and coronary arteries (outlined below). The common trunk gives rise to the pulmonary arteries, providing systemic, pulmonary, and coronary perfusion. It is characterized by a single great artery arising from the heart with a single semilunar valve that overrides the right and left ventricles. Persistent truncus arteriosus results from incomplete or failed septation. Truncus arteriosus has an estimated birth incidence of approximately 7 to 21 per 100,000 live births.ĭuring fetal development, the embryonic truncus arteriosus gives rise to the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Truncus arteriosus (TA) is a rare form of congenital heart disease occurring in 1-3% of patients with congenital heart disease. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return to the Coronary Sinus (TAPVR to CS).Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Arteries (ccTGA).
Left Superior Vena Cava to Coronary Sinus (LSVC to CS).Tetralogy of Fallot with Pulmonary Atresia (TOF/PA).Pulmonary Atresia with Intact Ventricular Septum (PA/IVS).Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve.Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs).Infracardiac Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
